
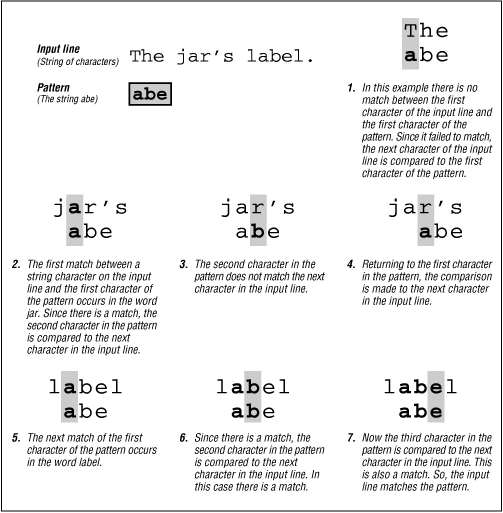
"them theme", "them them" in "them theme them them" The match must occur on a boundary between a \w (alphanumeric) and a \W (nonalphanumeric) character. The match must occur at the point where the previous match ended. The match must occur at the end of the string. The match must occur at the end of the string or before \n at the end of the string. The match must occur at the start of the string. Assertionīy default, the match must start at the beginning of the string in multiline mode, it must start at the beginning of the line.īy default, the match must occur at the end of the string or before \n at the end of the string in multiline mode, it must occur before the end of the line or before \n at the end of the line. The metacharacters listed in the following table are anchors. Matches any character other than a decimal digit.Īnchors, or atomic zero-width assertions, cause a match to succeed or fail depending on the current position in the string, but they do not cause the engine to advance through the string or consume characters. Matches any single character that is not in the Unicode general category or named block specified by name. Matches any single character in the Unicode general category or named block specified by name. or \u002E), you must precede it with the escape character ( \.). Wildcard: Matches any single character except \n. By default, characters in character_group are case-sensitive.Ĭharacter range: Matches any single character in the range from first to last.
Negation: Matches any single character that is not in character_group. Matches any single character in character_group. For more information, see Character Classes. Character classes include the language elements listed in the following table. This allows the regular expression engine to disambiguate language elements (such as * or ?) and character literals (represented by \* or \?).Ī character class matches any one of a set of characters. For example, \* is the same as \x2A, and \. When followed by a character that is not recognized as an escaped character in this and other tables in this topic, matches that character. Matches a Unicode character by using hexadecimal representation (exactly four digits, as represented by nnnn). Matches the ASCII control character that is specified by X or x, where X or x is the letter of the control character. Uses hexadecimal representation to specify a character ( nn consists of exactly two digits). Uses octal representation to specify a character ( nnn consists of two or three digits). "\r\nThese" in "\r\nThese are\ntwo lines." ( \r is not equivalent to the newline character, \n.) In a character class, matches a backspace, \u0008. For more information, see Character Escapes.
The backslash character (\) in a regular expression indicates that the character that follows it either is a special character (as shown in the following table), or should be interpreted literally.
#Regular expression not character download
We've also provided this information in two formats that you can download and print for easy reference: NET Regular Expressions.Įach section in this quick reference lists a particular category of characters, operators, and constructs that you can use to define regular expressions.

A pattern consists of one or more character literals, operators, or constructs. A regular expression to match the IP address 0.0.0.A regular expression is a pattern that the regular expression engine attempts to match in input text. When regular expressions sees a backslash, it knows that it should interpret the next character literally. In order to tell regular expressions to see the dot in its original context as a separator for the different parts of the IP address and not as a special character used to match any other character, you need to provide a signal to that effect. For example, the regular expression 0.0.0.0 matches: If you were to provide an IP address as a regular expression, you would get unpredictable results. Regular expressions first evaluates a special character in the context of regular expressions: if it sees a dot, then it knows to match any one character.įor example, the regular expression 1. In mathematics, the decimal point (.) is used to separate the whole part of a number from the fractional part. In written language, the period (.) is used to indicate the end of a sentence. For example, in regular expressions, the dot (.) is a special character used to match any one character. Some characters have one meaning in regular expressions and completely different meanings in other contexts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
